Miami Traumatic Brain Injury Lawyer
PROTECTING YOUR RIGHTS SINCE 1983
The traumatic brain injury lawyers at Bernstein & Maryanoff Injury Attorneys have the skill and knowledge needed to get the you top compensation for your traumatic brain injuries.
Legal Counsel for Brain Injury Accidents
With offices in Miami and across Florida, the law firm of Bernstein & Maryanoff Injury Attorneys has the resources and experience to take on the most complex brain injury cases. The firm’s attorneys and staff are dedicated to helping each client pursue the maximum compensation for their losses.
Depending on the severity and location of the injury, the effects of a brain injury can range from a minor annoyance to very serious and life-threatening. The study and diagnosis of head injuries are very complex. There may be overt signs of the injury such as loss of speech and motor skills, or there may only be more subtle personality changes. If you or a loved one have suffered a brain injury you should contact a lawyer with experience representing clients in brain injury-related legal claims to discuss your options.
The Brain and its Functions
The brain is the control center of the human body. It can be described as a bundle of gelatinous nervous system material floating in a protective sea of cerebrospinal fluid. The fluid acts as a shock absorber that dampens movement of the brain when a person is jolted. All of this fluid is encased inside of the human skull, which acts as a protective shell. The outside of the skull is smooth, but the inside is rough and boney. It is these rough, boney structures inside the skull that can injure the brain when a person is struck or jolted.
The brain is a sensory processor. This means that the brain controls thought, smell, sight, memory, and touch. In addition, the brain controls vital bodily functions such as walking, talking, breathing, and heart rate.
The Brain is divided into Three Main Parts:
Cerebrum
The cerebrum is the largest section of the brain. Different parts of the cerebrum are related to the control of cognitive abilities, memory, motor function, learning and speech.
Cerebellum
The cerebellum is a part of the hindbrain. It coordinates voluntary and involuntary muscle movements.
Brain Stem
The brain stem is the lower extension of the brain. It acts as a relay station between incoming stimulus and the rest of the brain.
Effects of a Head Injury
The effects of a brain injury largely depend on the severity of the injury, and the location of the affected part of the brain. All head injuries have the potential to be serious.
Concussion
A concussion is the common result of a blow to the head or a sudden deceleration. It results from a jarring of the brain. A concussion is graded according to its severity; depending on the loss of consciousness, amnesia and loss of equilibrium. A concussion often results in a period of altered consciousness during which the person is dazed or disoriented.
The common early symptoms of a concussion include:
- Dizziness
- Vertigo, or loss of equilibrium
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache
While many consider a concussion a minor annoyance, any head injury has the potential for serious long-term effects. The long-term effects of a head injury such as a concussion can greatly impact a person’s life.
Common long-term effects of a brain injury involving concussion are:
- Headaches
- Difficulty sleeping
- Lightheadedness
- Poor memory
- Depression
- Ringing in ears
- Poor concentration
- Slowed reaction time
- Intolerance to loud noise
- Mood swings and altered personality
- Difficulty choosing words
Comas
A severe head injury may also cause a coma. Coma is defined as a state of unconsciousness from which the patient cannot be awakened or aroused, even by powerful stimulation.
Amnesia
Amnesia is generally defined as the loss of memory, or a period of forgetfulness. Anterograde amnesia is defined as the inability to remember events beginning with the onset of the injury. Retrograde amnesia is defined as the loss of memory regarding events preceding the injury.
Effects of Severe Brain Damage
When a brain injury is very severe it can dramatically affect the person’s ability to return to a normal life. Depending on the location and severity of the injury there may be physical and/or behavioral effects. A severe head injury can affect a person’s ability to work, learn, and interact with their family.
The following are possible physical effects:
- Difficulty with mobility and coordination
- Difficulty talking and communicating
- Severe headaches
- Difficulty with, or loss of, sensation
The following are possible behavioral effects:
- Personality changes
- Depression
- Short attention span
- Learning difficulty
- Memory difficulty
The Causes of Brain Injuries
The brain is central to thought, movement, emotion, and vital bodily functions. Brain injuries may occur through work-related accidents, car accidents, slip and fall injuries, diseases, or even from complications at birth. The potentially devastating effects of brain injuries are as widely varied as the injuries that cause them. If you or a loved one have suffered a brain injury you should contact a lawyer who has experience in brain injury-related legal claims to discuss your options.
Contact Traumatic Brain Injuries
A contact traumatic brain injury causes damage to the brain as a result of external force to the head. A contact traumatic brain injury can cause closed head injury, brain swelling, bruising of the brain tissue, or nerve tearing.
Traumatic brain injury may result from:
- Sports injuries
- Work-related injuries
- Slip-and-fall injuries
- Car accidents, or
- Violence and assault
Closed Head Injuries
A closed head injury is brain damage resulting from external force to the head that does not penetrate the skull. Even though an object may not penetrate the head the potential for injury is still high. In fact, a closed head injury is often more dangerous than a penetration injury. When the brain is jostled in its entirety there is a greater chance of more widespread damage than when compared to a penetration injury which typically affects only one area of the brain.
Nerve Shearing
A violent jolting of the head can cause nerve shearing. Nerve shear is defined as the tearing of the fragile nerve fibers in the brain. This type of injury can be difficult to diagnose, but the effects can be devastating.
Brain Swelling and Bruising
Brain swelling and bruising may result from a violent blow to the skull. After the head is hit, the brain can “bounce” off the inside of the skull. This may cause nerve shearing as well as swelling and bruising of nerve tissue. This swelling can create pressure inside of the head which in turn leads to compression of vital blood vessels, hindering the brain’s blood and oxygen supply.
Non-Contact Traumatic Brain Injuries
The brain may be injured as a result of a non-contact injury or disease. For example, certain parts of the brain may be injured during medical emergencies such as stroke or heart attack. Stroke (also know as cerebrovascular accident, or CVA) and heart attack may affect the brain’s blood and oxygen supply causing localized or even widespread brain damage. In addition, the brain may be injured as a result of a near-drowning, suffocation, or heart-stopping electrical shock.
There are many ways in which a person may suffer a head injury. Severe head injuries can result in brain damage, and in turn cause major life changes. Such injuries may result in compromised thought processes, altered moods, and mobility problems. If you, or a loved one, have suffered a brain injury you should contact a lawyer who is experienced in brain injury-related legal claims to discuss your options.
DISCLAIMER: This site and any information contained herein are intended for informational purposes only and should not be construed as legal advice. Seek competent legal counsel for brain injury case advice on any legal matter.
Proving and Treating a Brain Injury
A permanent brain injury may be difficult to recognize and prove. Many of the associated changes in a person’s behavior or personality can be very subtle. The earlier a brain injury is diagnosed, the earlier a person can begin a treatment program.
If you, or a loved one, have suffered a brain injury you should contact a lawyer with experience in brain injury-related legal claims to discuss your options.
Diagnostic Tools
Symptoms of brain damage can vary in type and severity. The effects largely depend on the degree of injury and the portion of the brain affected. In general, anyone who has sustained a serious blow to the head should see a doctor to determine if they should undergo diagnostic analysis.
There are a variety of physical, mental, and psychological tests that medical professionals use to determine the severity and effects of a brain injury. Following is a brief description of some diagnostic tools.
MRI
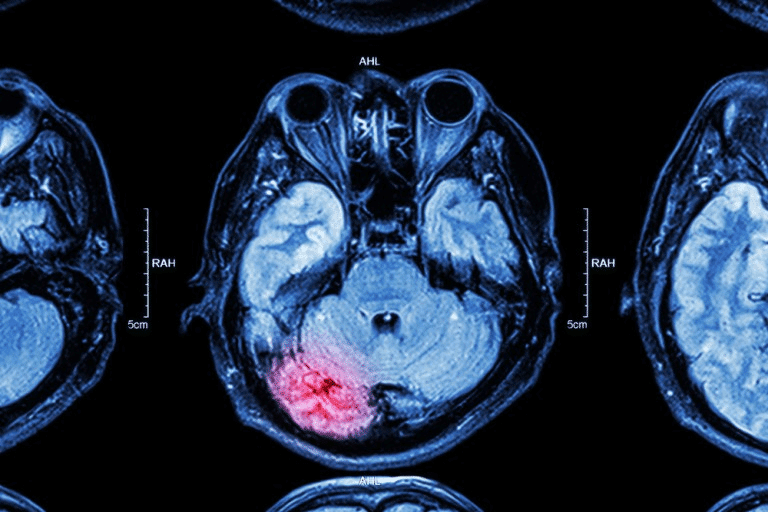
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive process that uses magnets to create nondestructive, three-dimensional, internal images of the soft tissues of the body. It is often used to analyze the brain, spinal cord and muscle.
CT Scan
A computed tomography (CT scan) is often referred to as a CAT scan. It is a computer-assisted x-ray procedure that produces cross-sectional images of the body. This procedure is usually noninvasive and brief in duration.
PET Scan
Positron Emission Tomography scanning (PET scan) uses a small amount of a radioactive tracer to create a view of a “slice” of a scanned object. This type of diagnostic tool is helpful for brain injury patients because it can show how and where the brain is functioning.
EEG
EEG is an abbreviation for an Electroencephalography procedure. An EEG is the graphic recording of electric waves created in the brain. It is recorded through surface electrodes that are placed on the scalp.
Functional Tests for Brain Damage
In addition to the abovementioned procedures, medical and psychological professionals use functional tests that analyze:
- Vision and eye movement
- Facial expression and reactions to stimuli
- Hearing
- Muscular movement
- Personality
- Memory
Treatment and Brain Injury Therapy
Treatment and therapy will greatly depend on the extent and nature of the injury. For example, a person may need physical and occupational rehabilitation to condition muscles and relearn life-skills. Generally, the earlier treatment begins the better.
Brain injuries can be devastating for both the person injured and their family. Therapy, medical treatments and supplies can be very expensive. A legal claim may help you secure financial assistance from the party responsible for the injury. If you or a loved one have suffered a brain injury you should contact a lawyer who is experienced in handling brain injury related legal claims to discuss your options.
DISCLAIMER: This site and any information contained herein are intended for informational purposes only and should not be construed as legal advice. Seek competent legal counsel for advice on any legal matter.





